Introduction
In the quest for a sustainable energy future, smart grid technology is revolutionizing how we generate, distribute, and consume electricity. By integrating advanced digital communication and automation, smart grids enhance the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of power systems. This article explores the transformative impact of smart grid technology on energy consumption, highlighting its key features, benefits, and real-world applications.
What is Smart Grid Technology?
Smart grid technology refers to an advanced electrical grid system that uses digital communication, automation, and information technology to manage electricity flow from generation to consumption. Unlike traditional grids, smart grids provide real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of energy use, leading to more efficient and sustainable power delivery.
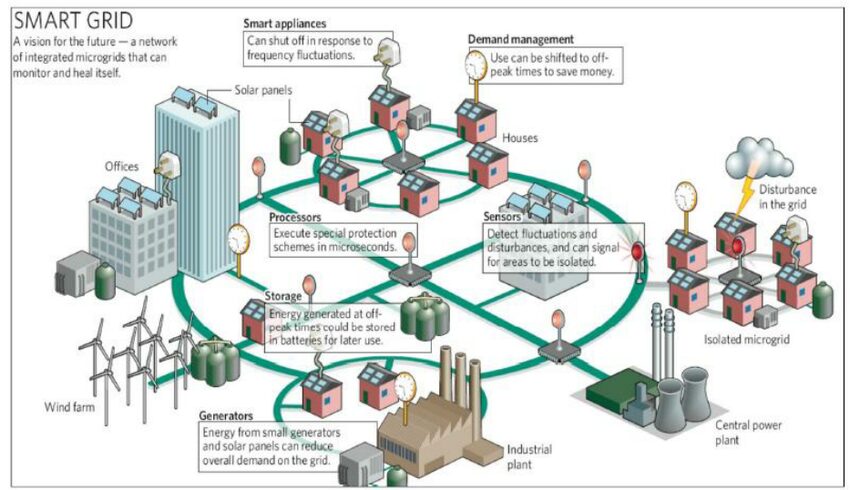
Key Features of Smart Grid Technology
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI):
- Smart Meters: These devices provide real-time data on energy consumption, enabling consumers to monitor and manage their usage more effectively.
- Two-Way Communication: Allows for real-time data exchange between utilities and consumers, facilitating demand response and dynamic pricing.
- Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) Integration:
- Renewable Energy Sources: Smart grids seamlessly integrate solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources, balancing supply and demand efficiently.
- Energy Storage Systems: Battery storage and other technologies store excess energy for use during peak demand periods.
- Grid Automation and Control:
- Sensors and Actuators: Deployed across the grid to monitor and control electrical flow, detect faults, and improve reliability.
- Advanced Control Systems: Utilize data analytics and machine learning to optimize grid performance and predict potential issues.
- Demand Response Programs:
- Dynamic Pricing: Encourages consumers to reduce or shift their energy use during peak times by offering variable pricing based on demand.
- Automated Demand Response: Automatically adjusts power consumption of connected devices based on grid conditions and pricing signals.
Benefits of Smart Grid Technology
- Enhanced Efficiency:
- Reduces energy losses and optimizes power delivery, leading to lower operational costs and improved resource utilization.
- Enables consumers to make informed decisions about their energy use, promoting energy-saving behaviors.
- Improved Reliability and Resilience:
- Real-time monitoring and automated controls minimize outages and enhance grid stability.
- Rapid fault detection and isolation prevent widespread blackouts and reduce downtime.
- Environmental Sustainability:
- Facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
- Supports energy storage solutions that enhance the use of clean energy.
- Economic Benefits:
- Reduces operational costs for utilities through efficient grid management and maintenance.
- Provides consumers with cost-saving opportunities through dynamic pricing and demand response programs.
- Empowered Consumers:
- Real-time energy consumption data empowers consumers to manage their usage and reduce their energy bills.
- Encourages the adoption of energy-efficient appliances and renewable energy systems.

Real-World Applications and Success Stories
- Case Study: Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E)
- PG&E implemented a smart grid system that includes advanced metering infrastructure, distributed energy resources, and automated demand response programs.
- Result: Enhanced grid reliability, significant energy savings for consumers, and improved integration of renewable energy sources.
- Case Study: European Union Smart Grid Projects
- The EU has funded numerous smart grid projects to promote energy efficiency and renewable integration across member states.
- Result: Improved grid stability, reduced carbon emissions, and increased adoption of renewable energy technologies.
- Case Study: Smart Grid City, Boulder, Colorado
- Boulder implemented one of the first comprehensive smart grid systems in the US, featuring smart meters, automated controls, and renewable energy integration.
- Result: Increased energy efficiency, reduced outages, and a significant boost in renewable energy usage.
Conclusion
Smart grid technology is transforming the way we consume energy, offering unparalleled efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. By integrating advanced digital communication, automation, and renewable energy sources, smart grids pave the way for a cleaner and more resilient energy future. As we continue to innovate and expand smart grid infrastructure, the potential for creating a sustainable energy ecosystem becomes increasingly achievable.





